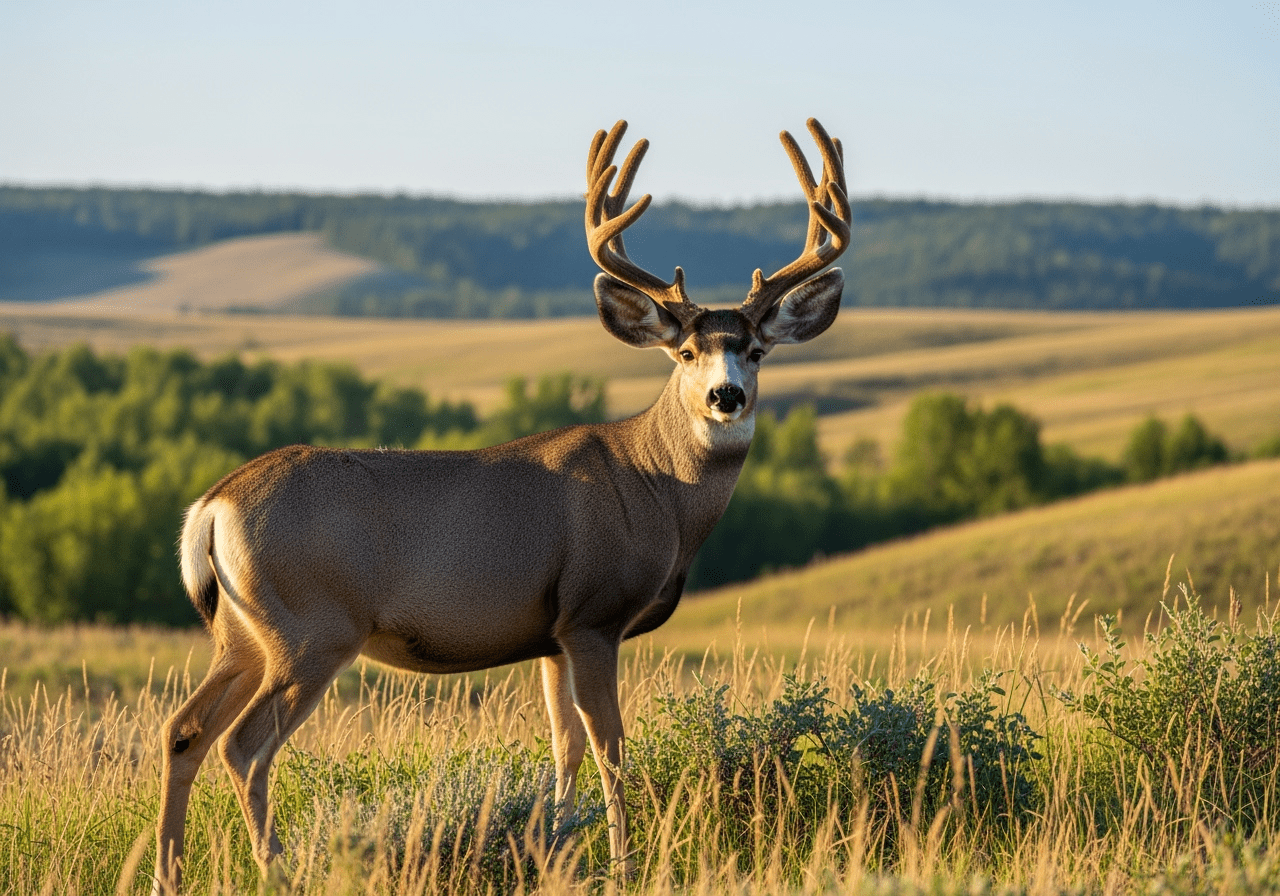
Migration Habits of Mule Deer in Alberta
Mule deer, a prominent species in Alberta, exhibit fascinating migration patterns that are closely tied to the changing seasons. These migrations are often driven by various environmental factors, including food availability, weather conditions, and the need for suitable breeding grounds. Typically, mule deer in Alberta begin their migration in the fall, as they seek out food resources to sustain themselves through the winter months. At this time, they often move from higher elevations and more open terrain in the mountains to lower valleys where forage is more abundant.
During the spring, the opposite migration occurs, as mule deer return to their summer ranges. These routes can be quite extensive, often covering several miles as they transition back to areas with lush vegetation, which is crucial for their nourishment. Research indicates that these deer tend to follow the same paths year after year, suggesting a strong instinctual connection to these migratory routes.
<p alberta="" also="" and="" are="" areas="" as="" availability="" avoid="" besides,="" bow="" but="" by="" conditions.
The understanding of mule deer migration in Alberta is important for conservation efforts. Recognizing their patterns helps in identifying critical habitats that require protection and management. This information is vital not only for wildlife enthusiasts but also for land managers aiming to maintain healthy ecosystems that support these magnificent creatures and their migratory behaviors.
Hunting Tips for Mule Deer
When pursuing mule deer, it is essential to understand their habits and preferences, which can significantly enhance your chances of success. Typically, the best times to hunt mule deer are during the early morning and late afternoon, as these animals are most active during these periods. Additionally, the peak seasons include the pre-rut and rut phases in the fall, particularly from late October to early November when male mule deer are more mobile and attentive to potential mates.
Identifying crucial habitats is another vital aspect of mule deer hunting. These animals often inhabit areas with a strong food source, including succulent grasses, shrubs, and grazing lands. Look for locations near water sources, as mule deer routinely visit these areas, especially during dry seasons. High-alpine meadows, dense forests, and rugged terrains are prime spots to consider. Familiarize yourself with local topography and vegetation to enhance your scouting efforts.
When it comes to effective hunting strategies, employing a combination of calls and scents can be particularly beneficial. Gruff grunt calls can attract male mule deer during the breeding season, while doe bleat calls can generate curiosity and provoke responses from nearby bucks. Scents such as doe estrus or an appropriate cover scent can further enhance your chances by masking human odor. Additionally, investing in appropriate camouflage gear is crucial, allowing you to blend seamlessly with the environment.
Finally, practice patience and remain mobile when hunting. Observing deer patterns and adapting your strategy accordingly can make a considerable difference in your success rate. Employing these tactics, alongside an understanding of mule deer behavior, will increase your prospects of harvesting this iconic species in the stunning landscapes of Alberta.
Tracking Tips for Mule Deer
Tracking mule deer requires an understanding of their habits and the ability to recognize various signs left in their environment. To effectively track these animals, hunters should familiarize themselves with specific indicators, such as tracks, droppings, and feeding areas. Mule deer tracks are typically heart-shaped and show distinct cloven hooves, which can help distinguish them from other deer species. Observing the depth and spacing of tracks can also provide insights into the deer’s size and movement patterns. Fresh tracks may indicate recent activity, offering a prime opportunity for hunters to pursue their quarry.
In addition to tracks, mule deer droppings present valuable information about their presence in an area. The droppings are usually pellet-shaped and can vary in size depending on the deer’s diet. Fresh droppings often indicate that deer have recently fed in the vicinity, making it a promising spot for hunters. Identifying feeding areas is crucial, as mule deer are known to frequent locations with abundant vegetation and foraging options. Open fields, agricultural lands, and areas with dense cover can all serve as feeding grounds.
Beyond physical signs, understanding mule deer behavior is essential for successful tracking. During the early morning and late evening hours, mule deer are most active, making these times ideal for hunters to engage in tracking efforts. Their tendency to move in small groups can also suggest that if one deer is spotted, more may be in the vicinity. Observing their social behavior, such as how they communicate through vocalizations and body language, can further inform tracking strategies. As hunters develop these skills, they will not only enhance their tracking abilities but significantly increase their chances of encountering mule deer in the wild.
Mule Deer vs. Whitetail: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between mule deer and whitetail deer is crucial for hunters in Alberta. These two species have distinct physical and behavioral characteristics that can significantly aid in identification during hunting excursions. One of the most noticeable physical differences lies in their antlers. Mule deer typically have broad, forked antlers that branch off from a central beam, which contrasts with the more traditionally shaped, spindly antlers of whitetail deer that often taper to a point. Additionally, the ear size varies; mule deer possess larger ears that are generally more elongated, which helps them in detecting sounds over long distances. In contrast, whitetail deer have smaller, more rounded ears.
The body structure plays an essential role in distinguishing these two species. Mule deer are generally larger and more robust, with a more pronounced hump over their shoulders, which gives them a distinctive profile. Whitetail deer, on the other hand, have a thinner, more streamlined body. This structural difference can be particularly evident when the animals are viewed from a distance.
Behaviorally, mule deer and whitetail deer exhibit different feeding habits and social structures. Mule deer are often found grazing actively in open spaces and are known for their unique ability to leap across obstacles. They are typically more solitary and less inclined to form large groups, preferring to remain in smaller family units. Whitetail deer tend to be more social and are frequently spotted in larger groups, especially in feeding areas during the fall and winter months. Understanding these differences in behavior can guide hunters, enabling them to adapt their strategies based on which species is present in a given area.
Natural Habitat of Mule Deer in Alberta
Mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) are widely recognized for their adaptability to various environments, making Alberta a prime location for these graceful mammals. They inhabit a range of ecosystems, including dense forests, open plains, and mountainous regions. Typically, mule deer thrive in mixed habitats that provide a balance between cover and forage. In forested regions, they prefer areas where understory vegetation is plentiful, allowing them to find food while maintaining a level of concealment from predators.
In addition to forested habitats, mule deer are often found in grasslands and shrublands, where they can graze on a variety of plants, particularly during spring and summer months when green shoots are abundant. The open plains of Alberta serve as critical feeding areas, particularly during the fall, as deer bulk up for winter. Mountainous regions also play a vital role in their habitat preferences, offering steep terrain that provides safety from both hunters and natural predators. These rugged areas are essential during the rutting season when male mule deer seek larger territories to assert dominance and attract mates.
Despite their ability to adapt to various habitats, mule deer populations face challenges due to habitat loss caused by urban development, agriculture, and climate change. These factors lead to fragmentation, reducing the connectivity of habitats essential for the migratory behaviors and genetic diversity of populations. Conservation efforts are crucial to mitigating these impacts, focusing on habitat restoration and protection practices. By enhancing corridors and preserving key areas, wildlife organizations in Alberta aim to secure the future of mule deer and ensure that hunters can continue to appreciate and pursue this iconic species in their natural habitat.
Seasonal Behaviors of Mule Deer
Mule deer, known for their large ears and distinctive forked antlers, exhibit notable behavioral changes throughout the seasons. Understanding these transformations is crucial for both wildlife enthusiasts and hunters aiming to optimize their excursions. The feeding habits of mule deer are profoundly influenced by seasonal shifts, as their diet changes based on the availability of vegetation. During the spring and summer months, mule deer primarily indulge in a diet rich in succulent greens, shrubs, and young shoots, which are abundant during this time. As autumn approaches, they begin to forage for acorns, nuts, and dry grasses, preparing themselves for the harsher winter conditions.
The breeding season, or rut, occurs in late fall, typically from late October to early December. This period is characterized by increased activity among males as they seek out females for mating. During this time, bucks can often be seen sparring with one another, establishing dominance within their social structure. This aggressive behavior is a crucial aspect of their seasonal dynamics, often leading to heightened visibility for those looking to hunt. Social structures among mule deer also transform throughout the seasons. In the summer, they tend to form larger groups, often including females, fawns, and bachelor groups of bucks. As fall approaches and the breeding season nears, these groups begin to fragment, with males becoming more solitary or forming smaller groups.
In winter, mule deer face additional challenges, such as food scarcity and harsh weather conditions. They adapt their behavior by seeking shelter in wooded or brushy areas to conserve energy and minimize exposure to the elements. Their movement patterns become less predictable, as they venture out primarily during dawn or dusk to feed, taking advantage of cooler temperatures. By understanding the seasonal behaviors of mule deer, hunters can time their trips more effectively, increasing the likelihood of a successful hunt while respecting the natural rhythms of these remarkable animals.
Ethical Hunting Practices for Mule Deer
Engaging in ethical hunting practices is paramount for the sustainability of mule deer populations. Ethical hunting embodies a commitment to respect wildlife, the ecosystem, and the regulations governing hunting activities. Central to this ethical framework is the principle of fair chase, which advocates for a hunting process that ensures a level playing field for both the hunter and the animal. This principle discourages the use of unsporting tactics, such as baiting or luring, and promotes a hunting experience that honors the skills and instincts of the mule deer.
Responsible harvesting practices are a critical aspect of ethical hunting. Hunters must engage in thorough planning and training, ensuring they are capable of making clean, humane shots that minimize suffering and waste. This involves understanding the anatomy of mule deer, practicing shooting skills, and utilizing appropriate equipment that is well-suited for the terrain and species. Furthermore, hunters should only take shots they are confident will result in a quick and ethical kill, thereby demonstrating a commitment to animal welfare.
Compliance with regulations set forth by Alberta’s wildlife authorities is essential for maintaining ecological balance. These regulations offer guidelines on hunting seasons, bag limits, and permissible methods, all designed to protect mule deer populations and their habitat. Staying informed about these regulations allows hunters to contribute positively to wildlife management efforts. Furthermore, supporting conservation initiatives and participating in community awareness programs can help promote sustainable hunting practices.
In summary, ethical hunting practices for mule deer hinge on the principles of fair chase, responsible harvesting, and adherence to established regulations. By committing to these practices, hunters not only enhance their own experience but also play a crucial role in ensuring the future sustainability of mule deer populations in Alberta.
Gear and Equipment for Hunting Mule Deer
When hunting mule deer, having the right gear and equipment can significantly influence the outcome of your hunting adventure. Whether you opt for a firearm or a bow, it is essential to choose equipment that aligns with both your preferences and the environment in which you will be hunting. Firearms are commonly favored for their range and accuracy, while bows offer a challenge that many hunters find rewarding. Each option has its merits, and understanding these can enhance your overall experience in the field.
In selecting a firearm, a rifle chambered in a caliber suitable for deer hunting, such as .243 Winchester or .30-06 Springfield, is recommended for its effectiveness and manageable recoil. On the other hand, if you prefer archery, a compound or recurve bow should be paired with the appropriate arrows and broadheads, tailoring your selection to the terrain and the distance from which you expect to take a shot.
Optics play a critical role in successfully spotting mule deer, known for their unique behavior and habitat preferences. A quality pair of binoculars, preferably with a magnification of 10x to 12x, can assist in identifying deer at a distance, while a high-quality scope can improve accurate shooting during your hunt. Choosing the appropriate clothing is equally important; layered, weather-appropriate attire not only keeps you comfortable but also helps you maintain a low profile in the natural surroundings.
Additionally, hunters should not overlook the necessity of scouting and pre-hunt preparation. Familiarizing yourself with the hunting area through scouting enhances your chances of spotting mule deer and understanding their patterns. Utilizing tools such as trail cameras, GPS devices, and maps can aid in planning your strategy, ensuring a more fruitful hunting expedition. Ensuring that you have the right gear and equipment, combined with thorough preparation, lays the groundwork for a successful and enjoyable hunt for mule deer in Alberta.
Mule Deer Conservation Efforts in Alberta
The conservation of mule deer populations in Alberta is a collective endeavor that involves the partnership of government agencies, non-profit organizations, and dedicated hunters. Recognizing the significance of maintaining healthy mule deer numbers, various initiatives have been put into place to ensure their survival and mitigate the threats they face, such as habitat loss and overharvesting.
Within the framework of Alberta’s wildlife management strategy, the provincial government actively monitors mule deer populations to gather data on their health and distribution. This information is vital in crafting effective management plans that aim to sustain these iconic animals. Various programs also focus on habitat restoration, as intact ecosystems are essential for the well-being of mule deer. These efforts often involve collaboration with organizations focused on wildlife conservation, such as the Alberta Conservation Association, which works on habitat enhancement projects and educational outreach to promote the importance of mule deer in the ecosystem.
Hunters play a crucial role in these conservation efforts. Through regulated hunting practices, they help maintain mule deer population levels, preventing overcrowding and habitat degradation. Programs that encourage selective harvest based on age and sex help ensure the continued survival of young and reproductive individuals. Moreover, many hunters participate in conservation programs that contribute a portion of their fees to habitat preservation, further intertwining hunting practices with conservation goals.
For individuals interested in supporting mule deer conservation, there are various avenues available, such as volunteering for habitat restoration projects, participating in citizen science initiatives, or advocating for policy changes to protect these animals and their habitats. By becoming involved in these efforts, individuals not only aid the survival of mule deer but also help foster a responsible hunting culture built on stewardship and sustainability.